Home > Reports and Articles > Reports > The role of industrial digitalisation in post-COVID-19 manufacturing recovery, diversification and resilience
Reports and articles
The role of industrial digitalisation in post-COVID-19 manufacturing recovery, diversification and resilience
Published on October 1st 2020
Key messages
- In simple terms, Industry 4.0 describes the widespread digitalisation of the manufacturing sector. In the past decade the shift to industrial digitalisation has largely been motivated by the desire to boost productivity and growth in an increasingly competitive manufacturing landscape.
- Evidence from around the world shows that digitalisation can play a key role in the post-COVID-19 manufacturing recovery (i.e. resuming operations), diversification (i.e. exploring new products and new markets) and resilience (i.e. preparing for supply/demand shocks and operational risks).
- Alongside previous drivers for industrial digitalisation, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted several new drivers for accelerating the adoption of Industry 4.0 in the UK and the world, including:
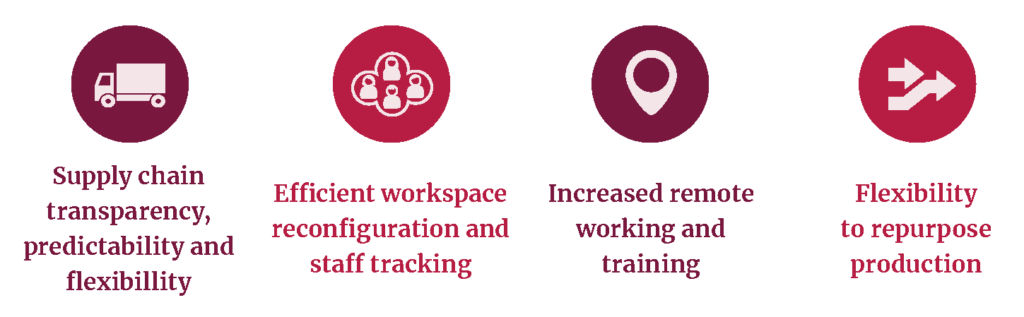
Figure 1. Emerging drivers of industrial digitalisation post-COVID-19
- In general, the international response to COVID-19 has been to accelerate industrial digitalisation across the entire manufacturing sector through existing or new horizontal measures.
- We find that countries are both reaffirming their previous commitments to Industry 4.0 technologies and creating new funding programmes and initiatives. For example:
- Japan is doubling down on support for automation in a bid to reshore manufacturing and support greater supply chain resilience.
- South Korea has pledged to roll out AI and 5G services, echoing previous commitments to expand AI and telecommunications infrastructure.
- Singapore’s existing “Go Digital” programme is being promoted to help businesses embrace digitalisation to overcome the challenges posed by the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Germany has established a €2 billion fund for start-ups and a €130 billion stimulus package, including additional loans and support for SMEs.
- China has announced a new plan to leverage digital technologies to resume production and support recovery focused on the development of remote working solutions and virus prevention and control solutions.
- Some national governments see industrial digitalisation as a potential source of social and employment safety net enhancements. For example, Korea’s “Digital New Deal” involves a $48 billion investment targeted at creating 903,000 jobs.
Key emerging messages, with implications for the UK Industrial Strategy, include the following:
- It is clear that the UK should not be the exception to this global trend towards industrial digitalisation. Further support is required to foster digital technology adoption to: employ workforce and visitor management solutions to ensure health and safety; enable digital workflows for remote working; implement intelligent supply chain forecasting to flexibly adjust production according to changes in demand; facilitate Project Defend reshoring through increased automation; and support green recovery and more sustainable forms of production in line with net zero directives.
- A wider roll-out of the Made Smarter programme must be a key policy priority for the UK in the short term. However, national rollout is a challenge because of the UK’s current institutional landscape. When analysing similar digital adoption initiatives internationally, it is clear that the institutional set-up of countries facilitates the national rollout of digital technology support programmes. A future UK industrial Strategy must emphasise the development of long-term regional structures to support digital technology adoption and innovation.
Others in this series
This policy brief is part of a series of studies produced for the Department for Business, Energy and Industry Strategy (BEIS), which include:
The contributors to this briefing note are: Lucia Corsini and David Leal-Ayala.
Related resources
News | 6th February 2026
UK Manufacturing Dashboard: latest performance and global benchmarks
Find out more
3rd February 2026
The Swiss paradox: a services reputation built on an industrial and innovation powerhouse
Find out more
News | 21st January 2026
CIIP delivers bespoke training for delegation from the Government of Nigeria
Find out more